The term "China Peru Mapa" represents a fascinating intersection of history, culture, and geography, highlighting the strong ties between two nations from vastly different parts of the globe: China and Peru. While at first glance, these countries might seem worlds apart, their shared history of migration, trade, and cultural exchange has created numerous unique connections worthy of exploration. The concept of a "map" in this context serves as both a literal and symbolic representation of these linkages.
Peru, known for its rich Incan heritage and breathtaking landscapes, is home to a significant Chinese diaspora that has profoundly influenced its cuisine, traditions, and economy. Similarly, China, a global superpower with a history spanning millennia, has fostered a growing interest in the cultural uniqueness of Peru. This mutual admiration has led to an increase in direct trade, tourism, and even shared diplomatic efforts. The "China Peru Mapa" thus becomes an emblem of this bilateral relationship, charting the ways these two nations intersect and influence one another.
In this article, we will delve into the multilayered connections between China and Peru, examining their shared history, cultural exchanges, and economic collaborations. From the geographic mapping of trade routes to the cultural "map" of shared traditions, this comprehensive guide will leave no stone unturned. Whether you're a geography enthusiast, a history buff, or someone curious about global cultural dynamics, this article offers valuable insights into the world of China Peru Mapa.
Read also:Toprated List Of Ulster County Restaurants For Every Food Lover
Table of Contents
- What is China Peru Mapa?
- Historical Ties Between China and Peru
- How Did Chinese Immigration Shape Peru?
- Cultural Synergies Between China and Peru
- China-Peru Economic Relations
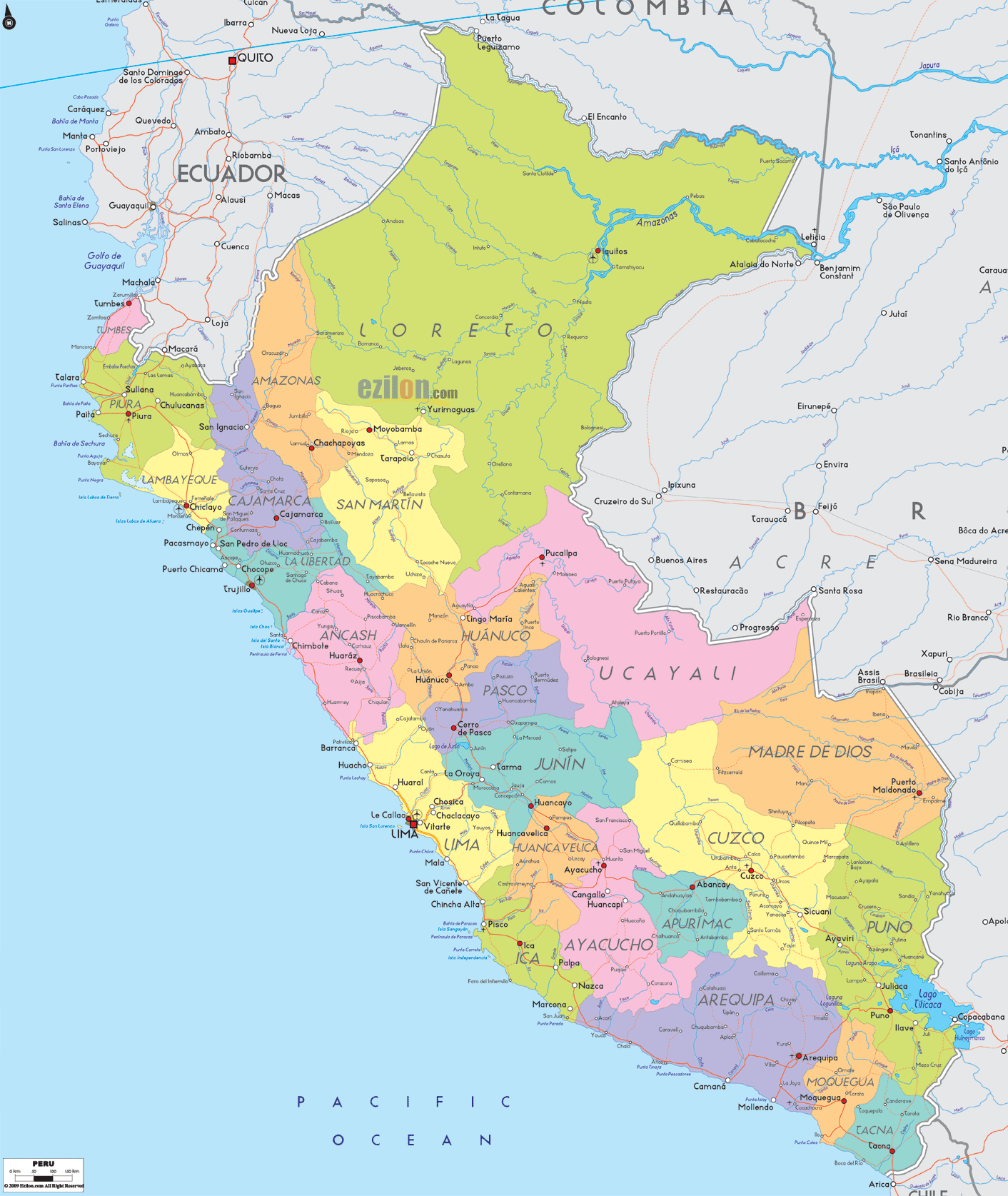
- Geographic Overview of China and Peru
- How Does the Geography of China and Peru Compare?
- Gastronomic Fusion Between China and Peru
- The Role of Trade Routes
- Diplomatic Relations Between China and Peru
- Mapping Tourism Between China and Peru
- Why Is the Chinese Community Vital to Peru?
- China and Peru in the Modern Era
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is China Peru Mapa?
The phrase “China Peru Mapa” is a confluence of geography and culture, symbolizing the intricate connections between one of the oldest civilizations in the world, China, and the vibrant South American nation of Peru. At its core, it represents how these two countries have mapped their historic ties, cultural exchanges, and economic collaborations over the years.
While the term may evoke a literal map delineating the geographic distance of nearly 19,000 kilometers (11,800 miles) between these nations, it also serves as a metaphorical map of their shared journeys. Through migration, trade, and mutual cultural appreciation, the "China Peru Mapa" highlights the evolving relationship between these two regions.
Why is it significant to understand this connection?
Understanding the China Peru Mapa allows us to appreciate the profound ways in which cultures can intersect and enrich one another. From the vast migration of Chinese laborers to Peru in the 19th century to the modern-day rise of China as Peru’s largest trading partner, these connections have shaped the identity of both nations.
What can we learn from this relationship?
The symbiotic relationship between China and Peru offers valuable lessons in globalization, mutual respect, and the benefits of cross-cultural collaboration. By studying the "China Peru Mapa," we can better understand how historical events and modern diplomacy influence the trajectory of international relations.
Historical Ties Between China and Peru
China and Peru’s historical connection dates back to the 19th century when the first wave of Chinese immigrants arrived in Peru. These laborers, referred to as "coolies," were brought to work in agriculture and railroads, filling a labor shortage created by the abolition of slavery. Over time, they formed one of the most significant Chinese diasporas in Latin America.
The Chinese community in Peru established "chifas," or Chinese-Peruvian restaurants, which became a cornerstone of Peruvian gastronomy. Their contributions to agriculture, commerce, and culture continue to shape Peru’s development. On the other hand, Peru became an important trading partner for China, supplying natural resources such as copper and fishmeal.
Read also:Centro Med Your Gateway To Comprehensive Healthcare Solutions
How did migration impact Peruvian society?
Migrants from China not only brought their labor but also their traditions, food, and entrepreneurial spirit. This cultural exchange laid the groundwork for the unique fusion of Chinese and Peruvian cultures that persists today.
What role did Chinese labor play in Peru’s economy?
Chinese laborers were instrumental in the development of Peru’s sugar plantations, railroads, and guano mining industry. Their hard work and resilience helped shape Peru’s infrastructure and economy during a critical period of growth.
How Did Chinese Immigration Shape Peru?
The immigration of Chinese laborers to Peru had a profound and lasting impact on the country. By integrating into Peruvian society, they brought their traditions, cuisine, and business acumen, leaving an indelible mark on the nation’s cultural and economic landscape.
- Chifa Cuisine: The blending of Chinese flavors with Peruvian ingredients gave birth to the iconic "chifa" cuisine, which is now a staple in Peru.
- Entrepreneurial Spirit: Many Chinese immigrants became successful business owners, contributing to Peru’s economic growth.
- Cultural Festivals: Traditional Chinese festivals, such as the Lunar New Year, are celebrated in Peru, reflecting the deep cultural integration of the Chinese community.
From the bustling streets of Lima’s Chinatown to the widespread popularity of Chinese dishes, the influence of Chinese immigrants is evident throughout Peru.
Cultural Synergies Between China and Peru
The cultural exchange between China and Peru is not a one-way street. While Chinese immigrants have enriched Peruvian culture, Peru has also influenced China, particularly through its unique traditions and historical treasures.
For instance, the growing interest of Chinese tourists in Machu Picchu and other Peruvian landmarks has fostered a deeper appreciation for Incan culture. Similarly, the popularity of Peruvian cuisine in China speaks to the mutual admiration between these two nations.
What are the standout examples of cultural fusion?
One of the standout examples of cultural fusion is the prevalence of "chifa" restaurants in Peru, which blend Chinese and Peruvian culinary traditions. Another is the shared celebration of festivals and the integration of Chinese herbal medicine into Peruvian practices.
How does this exchange benefit both nations?
The cultural exchange benefits both nations by fostering mutual respect and understanding. It also opens up opportunities for tourism, trade, and diplomatic collaboration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the China Peru Mapa and their answers:
- What does "China Peru Mapa" signify? It signifies the cultural, economic, and historical connections between China and Peru.
- Why is the Chinese community important to Peru? The Chinese community has significantly contributed to Peru’s economy, culture, and gastronomy.
- How does trade benefit both nations? Trade enriches both nations by providing resources and fostering economic growth.
- What is "chifa" cuisine? It is a fusion of Chinese and Peruvian culinary traditions.
- Are there any shared festivals between China and Peru? Yes, festivals like the Lunar New Year are celebrated in Peru.
- How has tourism influenced their relationship? Tourism has increased cultural appreciation and strengthened diplomatic ties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the "China Peru Mapa" represents a rich tapestry of cultural, economic, and geographic connections that continue to evolve. By understanding these ties, we gain valuable insights into the power of cultural exchange and the benefits of international collaboration.