ATF ATF is a term that holds multifaceted importance across various sectors, making it a pivotal subject for exploration. The acronym can stand for numerous things, depending on the context, such as Automatic Transmission Fluid, Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives, or even Air Traffic Flow. Each interpretation of ATF ATF carries its own weight and significance, influencing industries and regulatory frameworks worldwide. Understanding ATF ATF is crucial for anyone engaged in sectors where these entities play a role, as it can affect everything from mechanical operations to legal regulations and logistics.
Delving into the different aspects of ATF ATF, it becomes evident that this is not merely an acronym but a reflection of modern complexity in various fields. For instance, in the automotive industry, Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) is essential for the seamless functioning of vehicles, whereas in regulatory contexts, ATF signifies the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives, an agency that plays a vital role in enforcing laws related to these substances. Similarly, in aviation, ATF can relate to Air Traffic Flow, which ensures the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. Each aspect of ATF ATF underscores the necessity of specialized knowledge and adherence to standards and regulations to maintain safety, efficiency, and compliance.
The importance of ATF ATF cannot be overstated, as it intersects with daily life and professional practices in numerous ways. From ensuring that your car runs smoothly to maintaining public safety and facilitating international travel, ATF ATF encompasses a broad range of applications and implications. This article will explore these various dimensions of ATF ATF, providing a comprehensive insight into its importance, applications, and impacts across different sectors. By appreciating the multifaceted nature of ATF ATF, individuals and organizations can better align their practices with industry standards and regulatory requirements, ultimately fostering a more informed and compliant approach to their respective fields.
Read also:Majestic Wonders Of Arches National Park Utah A Complete Guide
Table of Contents
- What is ATF ATF?
- The Role of Automatic Transmission Fluid in Vehicles
- ATF: A Regulatory Perspective
- Managing Air Traffic Flow: A Critical Component
- Why is ATF ATF Important?
- Ensuring Mechanical Efficiency with ATF
- Navigating the Legal Framework of ATF
- Aviation Safety: The Role of ATF
- Common Misunderstandings About ATF ATF
- Future Trends and Innovations in ATF
- Applications of ATF ATF in Various Sectors
- Case Studies: ATF ATF in Action
- Challenges and Solutions with ATF ATF
- Frequently Asked Questions About ATF ATF
- Conclusion
What is ATF ATF?
ATF ATF can be a bit of a head-scratcher due to its diverse meanings across different fields. At its core, ATF refers to Automatic Transmission Fluid, Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives, or Air Traffic Flow. Each of these interpretations carries distinct significance and applications, making ATF ATF a term that is both multifaceted and crucial in various contexts. In the realm of automotive engineering, ATF is a hydraulic fluid essential for the operation of automatic transmissions. It ensures smooth gear shifts, reduces wear and tear, and prolongs the lifespan of the vehicle's transmission system.
From a regulatory standpoint, ATF represents the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives, a federal agency responsible for enforcing laws related to these substances in the United States. The agency plays a critical role in regulating the sale, possession, and transportation of firearms, as well as overseeing the compliance of alcohol and tobacco industries with federal regulations. This aspect of ATF ATF underscores its importance in maintaining public safety and order, particularly in relation to potentially hazardous or controlled substances.
In the field of aviation, ATF relates to Air Traffic Flow, an essential component of air traffic management that ensures the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. Proper management of air traffic flow is crucial for minimizing delays, optimizing flight routes, and maintaining safety standards within the aviation industry. Each of these interpretations of ATF ATF highlights the term's wide-ranging applications and the need for specialized knowledge and expertise in handling its various aspects.
The Role of Automatic Transmission Fluid in Vehicles
Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) plays a vital role in the performance and longevity of vehicles equipped with automatic transmissions. It serves multiple functions, including lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic pressure, all of which are essential for smooth and efficient gear changes. The right type and quality of ATF can significantly impact the performance of a vehicle's transmission system, influencing everything from fuel efficiency to overall driving experience.
ATF is specifically formulated to meet the unique requirements of automatic transmissions. It contains a blend of base oils and additives designed to provide optimal lubrication and protection against wear and tear. These additives enhance the fluid's performance by preventing oxidation, reducing friction, and protecting transmission components from corrosion. Choosing the correct ATF for a particular vehicle is crucial, as using the wrong type can lead to transmission malfunctions or even failure.
The maintenance of ATF levels and quality is an essential aspect of vehicle care. Regular checks and changes of transmission fluid can extend the life of the transmission and improve the vehicle's overall performance. Over time, ATF can become contaminated with debris and lose its effectiveness, which can lead to transmission problems if not addressed. Vehicle manufacturers typically provide guidelines on ATF maintenance, including recommended intervals for fluid changes and specific types of ATF suitable for their models.
Read also:Lori Ann Shevokas A Profile Of Inspiration And Achievements
ATF: A Regulatory Perspective
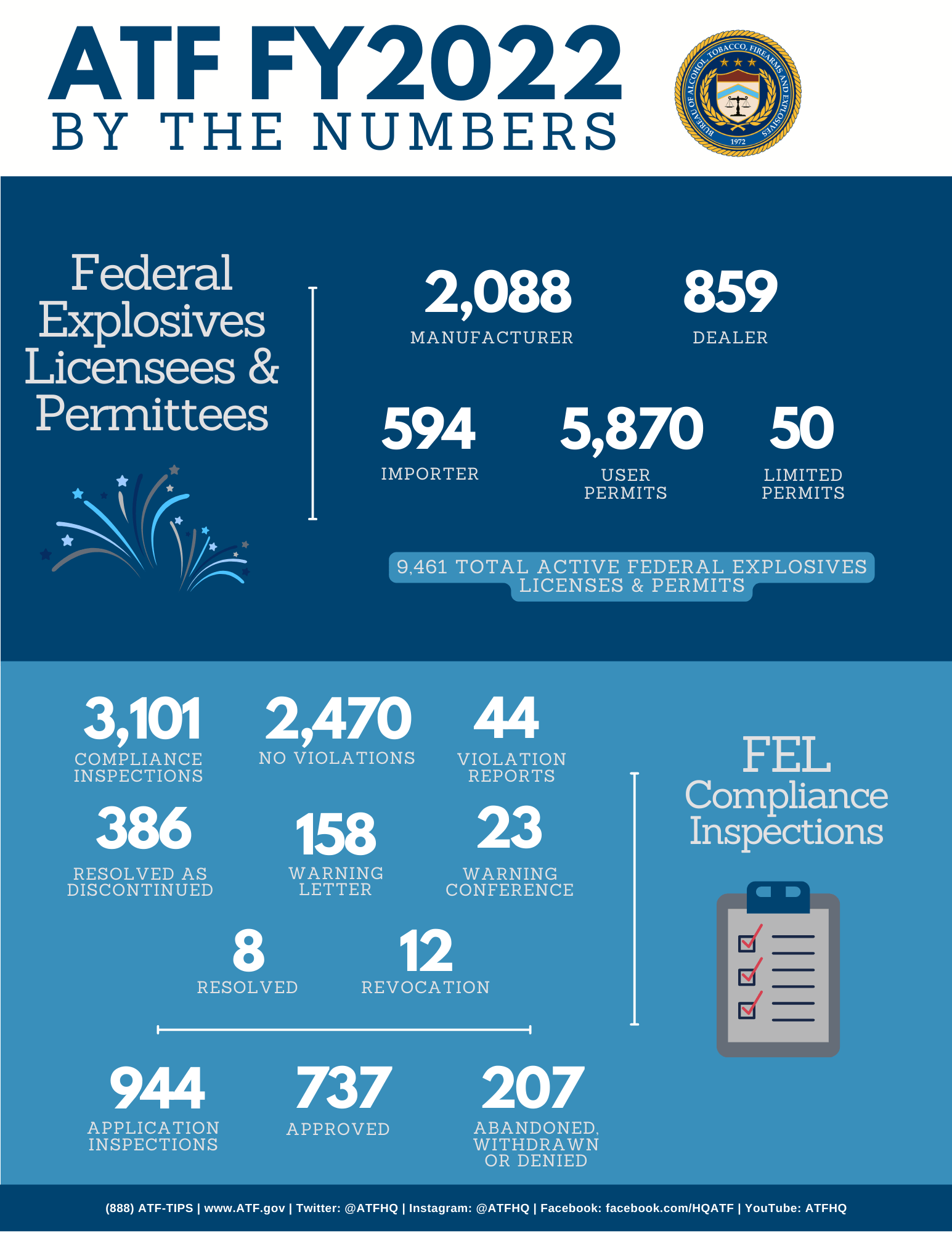
From a regulatory perspective, ATF stands for the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives, an agency within the United States Department of Justice. The ATF is tasked with enforcing federal laws and regulations related to alcohol, tobacco, firearms, explosives, and arson. Its mission is to protect communities from violent crimes, illegal trafficking of firearms and explosives, and the unlawful distribution of alcohol and tobacco products.
The ATF plays a critical role in regulating industries that deal with potentially dangerous or controlled substances. Its responsibilities include conducting investigations, monitoring compliance with federal laws, and providing training and resources to law enforcement agencies. The agency also collaborates with international partners to combat illegal trafficking and smuggling of firearms and explosives.
In addition to its enforcement duties, the ATF is involved in regulatory oversight and policy development. It issues licenses and permits for businesses and individuals engaged in the manufacture, sale, and distribution of firearms, alcohol, and tobacco products. The agency also develops guidelines and best practices for safe handling and storage of explosives and firearms, helping to ensure public safety and prevent accidents.
Managing Air Traffic Flow: A Critical Component
Air Traffic Flow (ATF) management is a crucial aspect of aviation operations, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft within the airspace. Proper management of air traffic flow is essential for minimizing flight delays, optimizing flight routes, and maintaining high safety standards in the aviation industry. This aspect of ATF ATF involves the coordination of multiple stakeholders, including air traffic controllers, airlines, and airport authorities, to achieve seamless and efficient air traffic operations.
Effective air traffic flow management relies on advanced technologies and systems that provide real-time data and analytics. These tools enable air traffic controllers to monitor and manage the movement of aircraft, predict potential congestion, and implement strategies to optimize traffic flow. The use of satellite-based navigation systems, radar, and communication technologies enhances the accuracy and efficiency of air traffic management, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall flight safety.
Air traffic flow management is also critical for environmental sustainability, as optimized flight routes and reduced delays can lead to decreased fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions. By implementing efficient air traffic flow strategies, the aviation industry can contribute to global efforts to reduce its environmental impact and promote sustainable practices. Continuous advancements in air traffic management technologies and processes are essential for addressing the growing demands of global air travel and ensuring the continued safety and efficiency of the aviation sector.
Why is ATF ATF Important?
ATF ATF holds significant importance due to its diverse applications and implications across various sectors. In the automotive industry, the proper use and maintenance of Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) are crucial for ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of vehicles. The right type of ATF can enhance fuel efficiency, improve driving experience, and prevent costly transmission repairs, making it a key component of vehicle maintenance.
From a regulatory standpoint, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) plays a vital role in maintaining public safety and enforcing laws related to controlled substances. The agency's efforts in regulating the sale, possession, and transportation of firearms, as well as overseeing the compliance of alcohol and tobacco industries, are essential for preventing illegal activities and safeguarding communities.
In aviation, effective air traffic flow management is critical for ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. Proper management of air traffic flow helps minimize delays, optimize flight routes, and maintain safety standards, contributing to the overall efficiency and sustainability of the aviation industry. The multifaceted nature of ATF ATF underscores its importance in modern dynamics and highlights the need for specialized knowledge and expertise in handling its various aspects.
Ensuring Mechanical Efficiency with ATF
Ensuring mechanical efficiency with Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) is essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of vehicles. ATF serves as a critical component in the operation of automatic transmissions, providing lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic pressure necessary for smooth and efficient gear shifts. Proper use and maintenance of ATF can significantly impact a vehicle's fuel efficiency, performance, and overall driving experience.
Regular maintenance of ATF levels and quality is a key aspect of vehicle care. Over time, ATF can become contaminated with debris and lose its effectiveness, leading to transmission problems if not addressed. Vehicle manufacturers typically provide guidelines on ATF maintenance, including recommended intervals for fluid changes and specific types of ATF suitable for their models. Adhering to these guidelines can help prevent costly transmission repairs and extend the life of the vehicle.
Choosing the right type of ATF is crucial, as using the wrong type can lead to transmission malfunctions or even failure. ATF is specifically formulated to meet the unique requirements of automatic transmissions, with a blend of base oils and additives designed to provide optimal lubrication and protection against wear and tear. These additives enhance the fluid's performance by preventing oxidation, reducing friction, and protecting transmission components from corrosion.
Navigating the Legal Framework of ATF
Navigating the legal framework of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) is essential for businesses and individuals involved in industries related to these substances. The ATF is responsible for enforcing federal laws and regulations related to alcohol, tobacco, firearms, explosives, and arson. Its mission is to protect communities from violent crimes, illegal trafficking, and unlawful distribution of these substances.
The ATF plays a critical role in regulating industries that deal with potentially dangerous or controlled substances. Its responsibilities include conducting investigations, monitoring compliance with federal laws, and providing training and resources to law enforcement agencies. The agency also collaborates with international partners to combat illegal trafficking and smuggling of firearms and explosives.
In addition to its enforcement duties, the ATF is involved in regulatory oversight and policy development. It issues licenses and permits for businesses and individuals engaged in the manufacture, sale, and distribution of firearms, alcohol, and tobacco products. The agency also develops guidelines and best practices for safe handling and storage of explosives and firearms, helping to ensure public safety and prevent accidents.
Aviation Safety: The Role of ATF
Aviation safety is paramount in the management of Air Traffic Flow (ATF), ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft within the airspace. Proper management of air traffic flow is essential for minimizing flight delays, optimizing flight routes, and maintaining high safety standards in the aviation industry. This aspect of ATF ATF involves the coordination of multiple stakeholders, including air traffic controllers, airlines, and airport authorities, to achieve seamless and efficient air traffic operations.
Effective air traffic flow management relies on advanced technologies and systems that provide real-time data and analytics. These tools enable air traffic controllers to monitor and manage the movement of aircraft, predict potential congestion, and implement strategies to optimize traffic flow. The use of satellite-based navigation systems, radar, and communication technologies enhances the accuracy and efficiency of air traffic management, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall flight safety.
Air traffic flow management is also critical for environmental sustainability, as optimized flight routes and reduced delays can lead to decreased fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions. By implementing efficient air traffic flow strategies, the aviation industry can contribute to global efforts to reduce its environmental impact and promote sustainable practices. Continuous advancements in air traffic management technologies and processes are essential for addressing the growing demands of global air travel and ensuring the continued safety and efficiency of the aviation sector.
Common Misunderstandings About ATF ATF
There are several common misunderstandings about ATF ATF, given its diverse meanings across different contexts. One of the most prevalent misconceptions is that ATF only refers to Automatic Transmission Fluid, overlooking its significance in other areas such as regulatory enforcement and aviation management. Understanding the various interpretations of ATF ATF is crucial for appreciating its multifaceted importance and implications in modern dynamics.
In the automotive industry, a common misunderstanding is that all ATF types are interchangeable. In reality, using the wrong type of ATF can lead to transmission malfunctions or even failure. Each vehicle model requires a specific type of ATF that meets its unique requirements, making it essential for vehicle owners to adhere to manufacturer guidelines for ATF selection and maintenance.
From a regulatory perspective, some people may not fully grasp the scope of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) responsibilities. The agency is tasked with enforcing federal laws related to these controlled substances, regulating industries, and ensuring public safety. Misunderstanding the ATF's role can lead to non-compliance with federal regulations, resulting in legal repercussions for businesses and individuals involved in these industries.
Future Trends and Innovations in ATF
The future of ATF ATF is characterized by continuous advancements and innovations across its various interpretations. In the automotive industry, the development of new ATF formulations and technologies aims to enhance the performance and efficiency of automatic transmissions. These innovations focus on reducing friction, improving thermal stability, and extending the lifespan of transmission systems, ultimately contributing to better fuel efficiency and driving experience.
From a regulatory standpoint, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) is expected to continue evolving its enforcement strategies and regulatory frameworks to address emerging challenges. This includes leveraging technology to improve compliance monitoring, enhancing collaboration with international partners, and developing new policies to address the evolving landscape of controlled substances and firearms.
In the aviation sector, advancements in air traffic flow management technologies and processes are essential for addressing the growing demands of global air travel. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics into air traffic management systems is expected to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of traffic flow management, reducing delays and improving safety standards. These innovations will play a crucial role in ensuring the continued safety, efficiency, and sustainability of the aviation industry.
Applications of ATF ATF in Various Sectors
ATF ATF finds applications across a wide range of sectors, each with its own unique set of requirements and implications. In the automotive industry, Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) is essential for the proper functioning of vehicles equipped with automatic transmissions. It ensures smooth gear shifts, reduces wear and tear, and prolongs the lifespan of the transmission system, making it a critical component of vehicle maintenance.
From a regulatory perspective, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) plays a vital role in enforcing laws related to controlled substances and firearms. Its responsibilities include regulating industries, conducting investigations, and ensuring compliance with federal laws, all of which are essential for maintaining public safety and preventing illegal activities.
In the aviation sector, effective management of Air Traffic Flow (ATF) is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. Proper air traffic flow management helps minimize delays, optimize flight routes, and maintain safety standards, contributing to the overall efficiency and sustainability of the aviation industry. Each of these applications of ATF ATF underscores its importance in modern dynamics and highlights the need for specialized knowledge and expertise in handling its various aspects.
Case Studies: ATF ATF in Action
Examining case studies of ATF ATF in action provides valuable insights into its real-world applications and implications. In the automotive industry, a notable case study involves the development and implementation of a new ATF formulation by a leading manufacturer. This innovative ATF was designed to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in hybrid and electric vehicles, demonstrating the potential for ATF advancements to contribute to sustainable transportation solutions.
From a regulatory perspective, a case study of the ATF's efforts to combat illegal firearms trafficking highlights the agency's critical role in enforcing federal laws and safeguarding communities. Through collaborative investigations and partnerships with international agencies, the ATF successfully dismantled a major firearms trafficking network, preventing illegal weapons from reaching criminal organizations.
In the aviation sector, a case study of a major airport's implementation of advanced air traffic flow management technologies showcases the benefits of optimizing air traffic operations. By leveraging real-time data and analytics, the airport was able to reduce flight delays, optimize flight routes, and enhance safety standards, ultimately improving overall efficiency and passenger satisfaction. These case studies illustrate the diverse applications and impacts of ATF ATF across different sectors.
Challenges and Solutions with ATF ATF
While ATF ATF offers numerous benefits across various sectors, it also presents certain challenges that require innovative solutions. In the automotive industry, one of the primary challenges is ensuring the compatibility of ATF with increasingly complex transmission systems. As vehicles become more advanced, the development of new ATF formulations that meet the specific requirements of different transmission types is essential for maintaining performance and efficiency.
From a regulatory standpoint, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) faces challenges in addressing the evolving landscape of controlled substances and firearms. The agency must continuously adapt its enforcement strategies and regulatory frameworks to keep pace with emerging threats and trends. Leveraging technology and enhancing collaboration with international partners are key solutions for overcoming these challenges and ensuring effective regulation.
In the aviation sector, managing air traffic flow in increasingly congested airspace presents a significant challenge. The integration of advanced technologies and systems into air traffic management processes is crucial for optimizing traffic flow and maintaining safety standards. Solutions such as the use of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of air traffic management, ultimately addressing the challenges of modern aviation dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions About ATF ATF
What does ATF stand for in the automotive industry?
In the automotive industry, ATF stands for Automatic Transmission Fluid, which is essential for the operation of vehicles with automatic transmissions.
What is the role of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF)?
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF) is a federal agency responsible for enforcing laws related to alcohol, tobacco, firearms, explosives, and arson, ensuring public safety and regulatory compliance.
How does air traffic flow management impact aviation safety?
Effective air traffic flow management ensures the safe and efficient movement of aircraft, minimizing delays, optimizing flight routes, and maintaining high safety standards in the aviation industry.
Can using the wrong type of ATF harm a vehicle's transmission?
Yes, using the wrong type of Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) can lead to transmission malfunctions or even failure, as each vehicle model requires a specific type of ATF that meets its unique requirements.
What challenges does the ATF face in regulating controlled substances and firearms?
The ATF faces challenges in addressing the evolving landscape of controlled substances and firearms, requiring continuous adaptation of enforcement strategies and regulatory frameworks to keep pace with emerging threats and trends.
How are advancements in air traffic flow management technologies benefiting aviation?
Advancements in air traffic flow management technologies, such as the integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics, enhance the accuracy and efficiency of traffic flow management, reducing delays and improving safety standards in aviation.
Conclusion
ATF ATF encapsulates a diverse range of meanings and applications, each with its own unique set of challenges and implications. Whether it pertains to Automatic Transmission Fluid in the automotive sector, the regulatory efforts of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives, or the management of Air Traffic Flow in aviation, ATF ATF plays a critical role in modern dynamics. Its significance is underscored by its impact on safety, efficiency, and compliance across different industries.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of ATF ATF is essential for individuals and organizations involved in these sectors. By appreciating its diverse interpretations and applications, stakeholders can better align their practices with industry standards and regulatory requirements, ultimately fostering a more informed and compliant approach to their respective fields. As advancements and innovations continue to shape the landscape of ATF ATF, staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating its complexities and leveraging its benefits.
In conclusion, ATF ATF is more than just an acronym; it is a reflection of the interconnectedness and complexity of modern industries. Its diverse meanings and applications highlight the need for specialized knowledge and expertise in handling its various aspects, ensuring that individuals and organizations can effectively navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by ATF ATF in today's dynamic world.