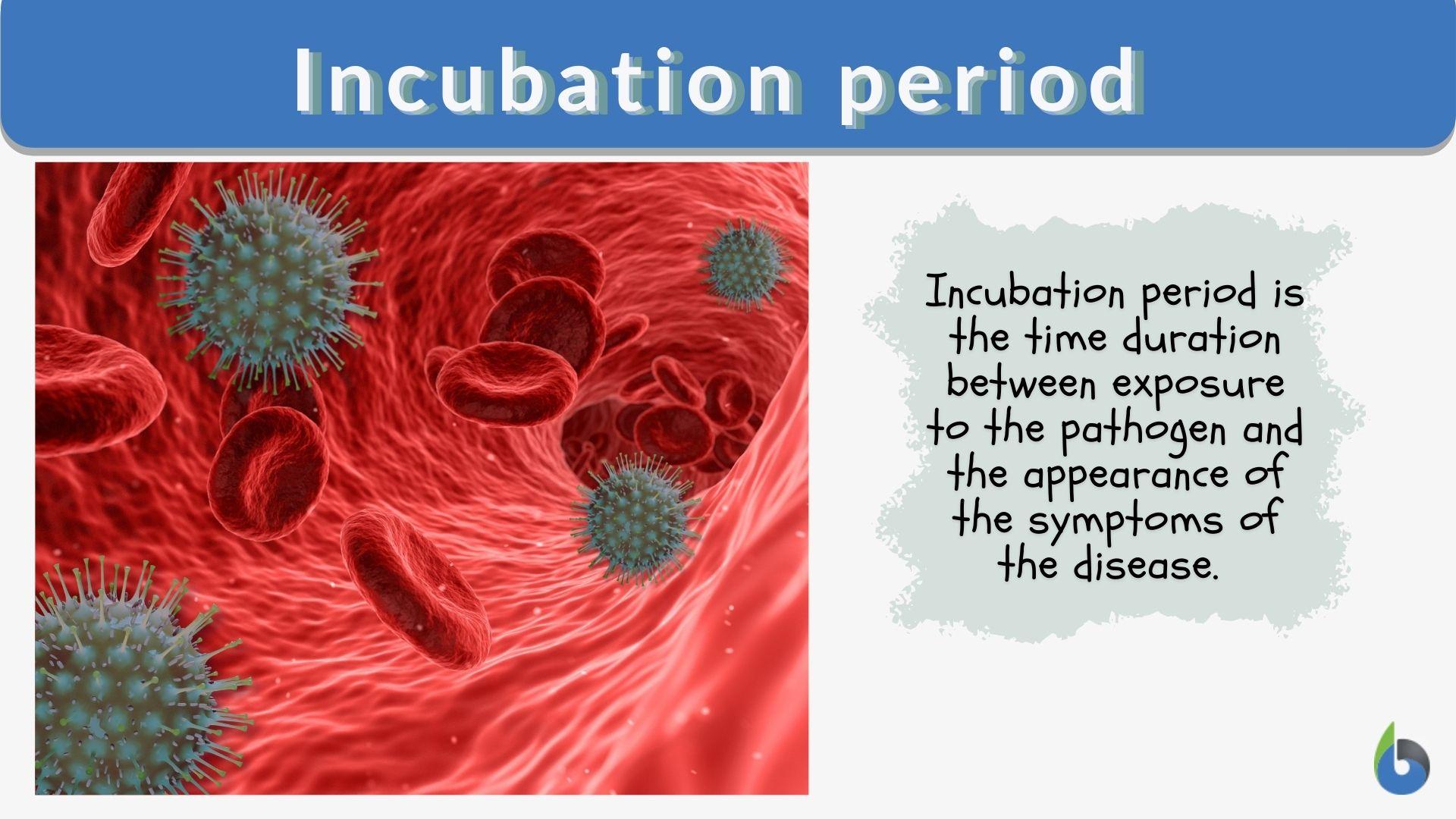
The term "jn.1 incubation period" refers to the time frame between the initial exposure to a particular pathogen and the onset of symptoms. Understanding this period is crucial for both medical professionals and the general public, as it provides insight into the spread and control of infectious diseases. Whether you're dealing with a virus, bacteria, or another pathogen, the incubation period can vary significantly, impacting how the disease is managed and contained.
In the realm of infectious diseases, the incubation period is a key factor that influences public health responses and individual behavior. Accurate information about the "jn.1 incubation period" can aid in the development of effective quarantine measures, guide medical treatment, and inform individuals about when they might be contagious. This knowledge is not only essential for healthcare providers but also for those who might be exposed to an infectious disease, allowing them to take appropriate precautions.
Moreover, understanding the nuances of the "jn.1 incubation period" can help in predicting the course of an outbreak, enabling public health officials to allocate resources effectively and prevent widespread transmission. By grasping the typical length of this period and recognizing the symptoms that may arise, individuals and communities can better prepare for and respond to potential health threats. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the jn.1 incubation period, exploring various facets that influence its duration and implications.
Read also:Uncover The Wonders Of Skyes Avi A Detailed Exploration
Table of Contents
- What is the Incubation Period?
- Factors Affecting the Incubation Period
- Examples of Incubation Periods in Common Diseases
- Why is the Incubation Period Important?
- How Does the Incubation Period Impact Disease Control?
- JN.1 Incubation Period in Viral Infections
- JN.1 Incubation Period in Bacterial Infections
- JN.1 Incubation Period and Symptom Onset
- The Role of JN.1 Incubation Period in Research
- JN.1 Incubation Period in Epidemic Modeling
- How to Minimize the Risk During the Incubation Period?
- JN.1 Incubation Period and Public Health Policies
- JN.1 Incubation Period: Implications for Individuals
- JN.1 Incubation Period and Vaccine Development
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is the Incubation Period?
The incubation period is the duration between exposure to an infectious agent and the appearance of the first symptoms. It is a critical phase in the lifecycle of infectious diseases, as it determines how quickly symptoms appear and how the disease progresses. This period can vary widely depending on the type of pathogen, mode of transmission, and individual host factors.
Understanding the incubation period is essential for diagnosis and treatment. It helps health professionals determine the likely source of an infection and assess the potential spread within a population. The length of the incubation period can also influence the effectiveness of quarantine measures and the timing of interventions to control an outbreak.
Factors Affecting the Incubation Period
Several factors can influence the length of the incubation period, including:
- Type of Pathogen: Different pathogens have varying incubation periods. For example, viruses may have shorter incubation periods compared to bacteria.
- Route of Transmission: The way a pathogen enters the body can affect how quickly symptoms appear. For instance, respiratory viruses may have shorter incubation periods due to rapid transmission through the air.
- Host Factors: Individual characteristics such as age, immune status, and overall health can impact the incubation period. A healthy immune system may be able to suppress the pathogen, delaying symptom onset.
- Environmental Factors: Conditions such as temperature and humidity can influence how quickly a pathogen replicates, affecting the incubation period.
Examples of Incubation Periods in Common Diseases
Different infectious diseases have distinct incubation periods. Here are some examples:
Viral Diseases
Viral infections often have brief incubation periods, allowing rapid transmission. Examples include:
- Influenza: Typically 1-4 days.
- Common Cold: Usually 1-3 days.
- COVID-19: Approximately 2-14 days.
Bacterial Diseases
Bacterial infections may have longer incubation periods, depending on the species and infection site. Examples include:
Read also:Essential Guide To Dona Ana County Inmates Laws Rights And System Overview
- Tuberculosis: Typically 2-12 weeks.
- Salmonella: Usually 6-72 hours.
- Strep Throat: Approximately 2-5 days.
Why is the Incubation Period Important?
The incubation period is crucial for several reasons:
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Knowing the incubation period can help healthcare providers diagnose infections more accurately and initiate timely treatment.
- Public Health Measures: Understanding the incubation period aids in designing effective quarantine protocols and controlling outbreaks.
- Contact Tracing: Accurate knowledge of the incubation period helps in identifying and notifying contacts who may have been exposed to an infectious disease.
How Does the Incubation Period Impact Disease Control?
The incubation period significantly influences disease control strategies. Here's how:
- Quarantine and Isolation: The length of the incubation period determines the duration of quarantine and isolation measures to prevent transmission.
- Timing of Interventions: Early intervention can halt the spread of a disease. Understanding the incubation period helps in implementing timely measures.
- Resource Allocation: Public health resources can be allocated more efficiently when the incubation period is known, ensuring preparedness for potential outbreaks.
JN.1 Incubation Period in Viral Infections
The "jn.1 incubation period" in viral infections varies depending on the virus type and transmission route. Common viral infections like influenza and COVID-19 have distinct incubation periods, which affect how they spread and are managed.
For example, influenza typically has a short incubation period of 1-4 days, leading to rapid symptom onset and transmission. In contrast, COVID-19 has a longer incubation period, averaging 2-14 days, allowing for asymptomatic spread and complicating containment efforts.
JN.1 Incubation Period in Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections often have more varied incubation periods, influenced by the species and infection site. For instance, tuberculosis has a prolonged incubation period, ranging from 2 to 12 weeks, complicating diagnosis and treatment.
Conversely, bacterial infections like salmonella have relatively shorter incubation periods, typically 6-72 hours, leading to rapid symptom development and transmission. Understanding these variations is vital for effective diagnosis and control measures.
JN.1 Incubation Period and Symptom Onset
The onset of symptoms is directly linked to the "jn.1 incubation period." The timing of symptom appearance can vary, impacting diagnosis and treatment strategies. Recognizing early symptoms is crucial for prompt intervention and preventing disease spread.
For instance, early recognition of COVID-19 symptoms during the incubation period can lead to timely testing and isolation, reducing transmission risk. Similarly, understanding the incubation period for diseases like measles can facilitate early vaccination and protection measures.
The Role of JN.1 Incubation Period in Research
Research into the "jn.1 incubation period" is essential for understanding disease dynamics and improving public health responses. Studies on incubation periods provide valuable insights into how diseases spread and evolve, informing prevention and treatment strategies.
For example, research on the incubation period of emerging viruses helps predict potential outbreaks and develop effective vaccines. This knowledge is crucial for preparing for future pandemics and mitigating their impact on global health.
JN.1 Incubation Period in Epidemic Modeling
Epidemic modeling relies heavily on accurate data about the "jn.1 incubation period." Models use this information to simulate disease spread and predict the course of an outbreak, guiding public health interventions.
Accurate modeling can help identify high-risk areas, allocate resources effectively, and implement targeted measures to control disease transmission. Understanding the incubation period is thus vital for developing effective epidemic response plans.
How to Minimize the Risk During the Incubation Period?
Minimizing risk during the "jn.1 incubation period" involves several strategies:
- Practicing Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and sanitization can reduce the risk of transmission.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance from others can prevent exposure to infectious agents.
- Wearing Masks: Masks can limit the spread of respiratory infections, especially during the incubation period.
- Timely Testing: Early testing can identify infections during the incubation period, allowing for prompt isolation and treatment.
JN.1 Incubation Period and Public Health Policies
Public health policies are often shaped by understanding the "jn.1 incubation period." Effective policies can mitigate the impact of infectious diseases and protect public health.
For example, quarantine policies are designed based on the incubation period to prevent transmission. Vaccination campaigns are also timed to provide immunity before the onset of symptoms, reducing the risk of outbreaks.
JN.1 Incubation Period: Implications for Individuals
For individuals, understanding the "jn.1 incubation period" is crucial for protecting themselves and their communities. Awareness of the incubation period can guide personal health decisions and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Individuals can take proactive measures, such as self-isolating if exposed to an infectious agent, seeking medical advice, and adhering to public health guidelines. These actions can significantly reduce the risk of transmission and protect vulnerable populations.
JN.1 Incubation Period and Vaccine Development
Vaccine development often considers the "jn.1 incubation period" to ensure efficacy and safety. Understanding the incubation period helps researchers design vaccines that provide immunity before the onset of symptoms, enhancing their protective effects.
For example, vaccines for diseases like measles and influenza are developed with the incubation period in mind, ensuring early protection and reducing the risk of outbreaks. This knowledge is critical for developing effective vaccines and combating infectious diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the typical length of the jn.1 incubation period?
The "jn.1 incubation period" varies depending on the pathogen and host factors. It can range from a few days to several weeks.
- How does the incubation period affect quarantine measures?
The incubation period determines the duration of quarantine and isolation measures to prevent disease spread.
- Can the incubation period vary between individuals?
Yes, individual factors such as age, immune status, and health can influence the length of the incubation period.
- Why is understanding the incubation period important for vaccine development?
Understanding the incubation period helps design vaccines that provide immunity before symptoms appear, enhancing their effectiveness.
- How do environmental factors impact the incubation period?
Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity can affect pathogen replication, influencing the incubation period.
- What role does the incubation period play in epidemic modeling?
The incubation period is a key factor in epidemic models, which use this data to simulate disease spread and guide interventions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the "jn.1 incubation period" is vital for managing infectious diseases and protecting public health. This period influences diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies, shaping public health policies and individual behavior. By recognizing the factors that affect the incubation period and its implications, individuals and communities can better prepare for and respond to potential health threats. This knowledge is essential for controlling outbreaks, developing effective vaccines, and ensuring global health security.