India is a nation of remarkable diversity, and this is perhaps most evident in its languages. With over a billion people spread across its vast landscapes, the linguistic tapestry of India is as colorful and intricate as its cultural heritage. The question "how many languages are there in India?" might seem simple, but the answer is surprisingly complex, reflecting centuries of history, migration, and regional identities.
Languages in India are not just a means of communication but a profound expression of identity, tradition, and community. The Indian Constitution recognizes multiple languages, and the country is home to thousands of dialects and mother tongues. From the classical beauty of Sanskrit to the modern vibrancy of Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, and countless others, India’s linguistic wealth is unparalleled. Each language carries with it stories, customs, and a unique worldview, making the study of Indian languages a fascinating subject.
In this article, we’ll delve into the incredible linguistic diversity of India, exploring how languages are classified, how many are officially recognized, the role of regional languages, endangered tongues, and much more. By the end, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation of the linguistic heritage that binds this multicultural nation together. Let’s get started!
Read also:Rock Icon Susi Quatro A Musical Force
Table of Contents
- What Defines a Language?
- How Are Languages Classified in India?
- How Many Languages Are Officially Recognized?
- How Many Languages Are There in India?
- Regional Languages and Their Cultural Significance
- Role of Hindi and English in India
- What Are Scheduled Languages in India?
- Endangered and Lost Languages
- How Do Languages Impact Education in India?
- Role of Linguistic Diversity in Governance
- How Do Languages Impact Indian Culture?
- Languages and Technology in India
- Why Are Some Indian Dialects Misunderstood as Languages?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Defines a Language?
Languages are more than just words and grammar. They are systems of communication that encompass vocabulary, syntax, phonetics, and semantics. In India, the distinction between a language and a dialect often blurs, as regional variations can be so distinct that they might qualify as separate languages. UNESCO defines a language as a structured system of communication used by a particular community or culture.
In the Indian context, a language is often tied to its script, cultural practices, and historical significance. For example, Hindi and Urdu share the same linguistic roots but are considered separate languages due to their scripts (Devanagari for Hindi and Perso-Arabic for Urdu) and cultural associations.
How Are Languages Classified in India?
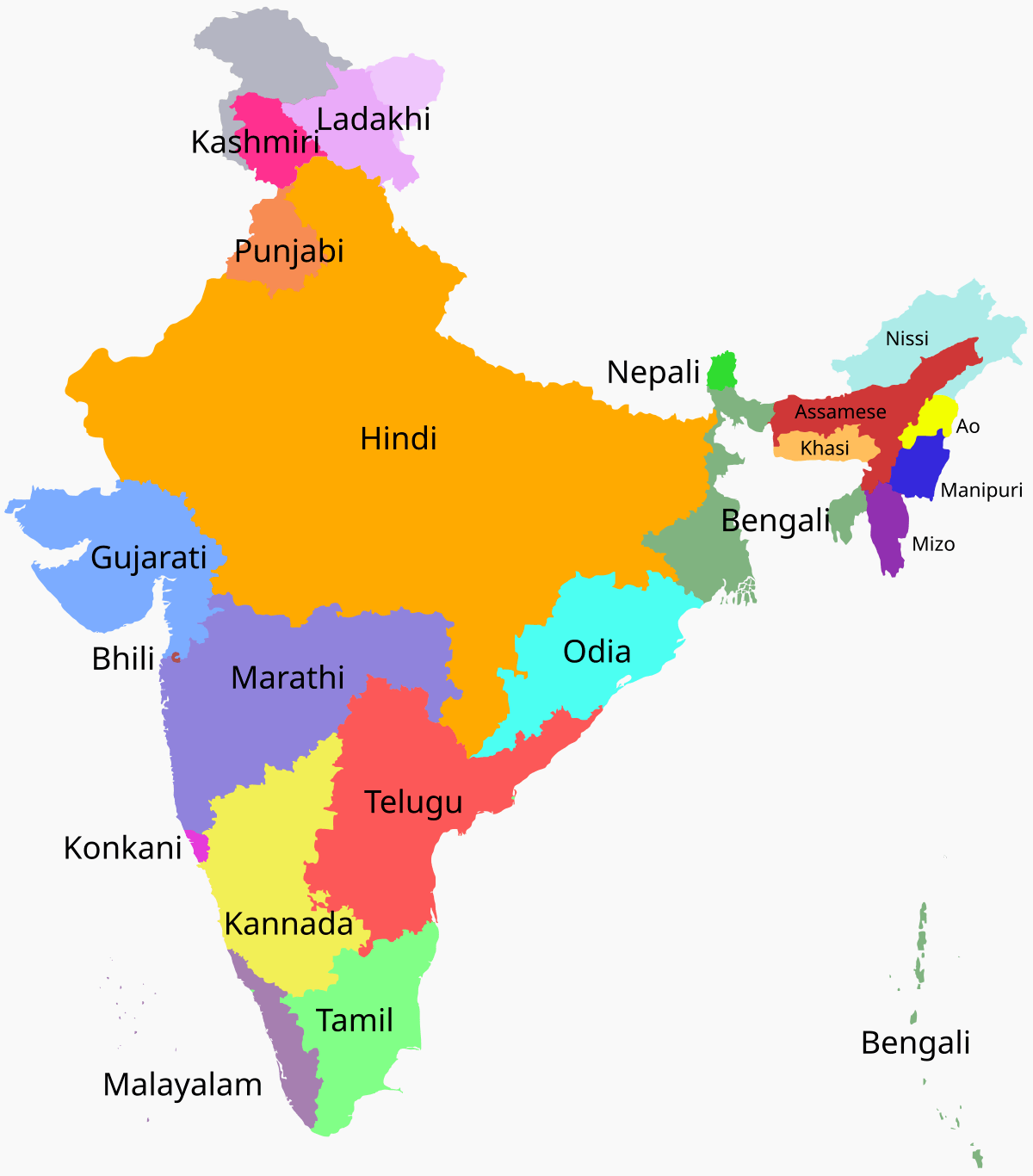
Languages in India can be broadly classified into four major families:
- Indo-Aryan: Spoken predominantly in North and Central India, languages like Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, and Punjabi belong to this family.
- Dravidian: Found mainly in South India, this family includes Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
- Austroasiatic: Spoken by tribal communities, languages like Santali and Khasi belong to this group.
- Sino-Tibetan: Found in the northeastern states, this family includes languages like Manipuri and Bodo.
Beyond these families, there are isolated languages like Nihali and Burushaski, which don’t easily fit into any category.
How Many Languages Are Officially Recognized?
India’s Constitution recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule, known as the "Scheduled Languages." These include widely spoken languages like Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil, as well as regional languages like Konkani and Sindhi. Additionally, English and Hindi are used for official purposes at the national level.
Here’s a list of the Scheduled Languages:
Read also:All You Need To Know About Neck Bones Structure Function And Health
- Assamese
- Bengali
- Bodo
- Dogri
- Gujarati
- Hindi
- Kannada
- Kashmiri
- Konkani
- Maithili
- Malayalam
- Manipuri
- Marathi
- Nepali
- Odia
- Punjabi
- Sanskrit
- Santali
- Sindhi
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Urdu
How Many Languages Are There in India?
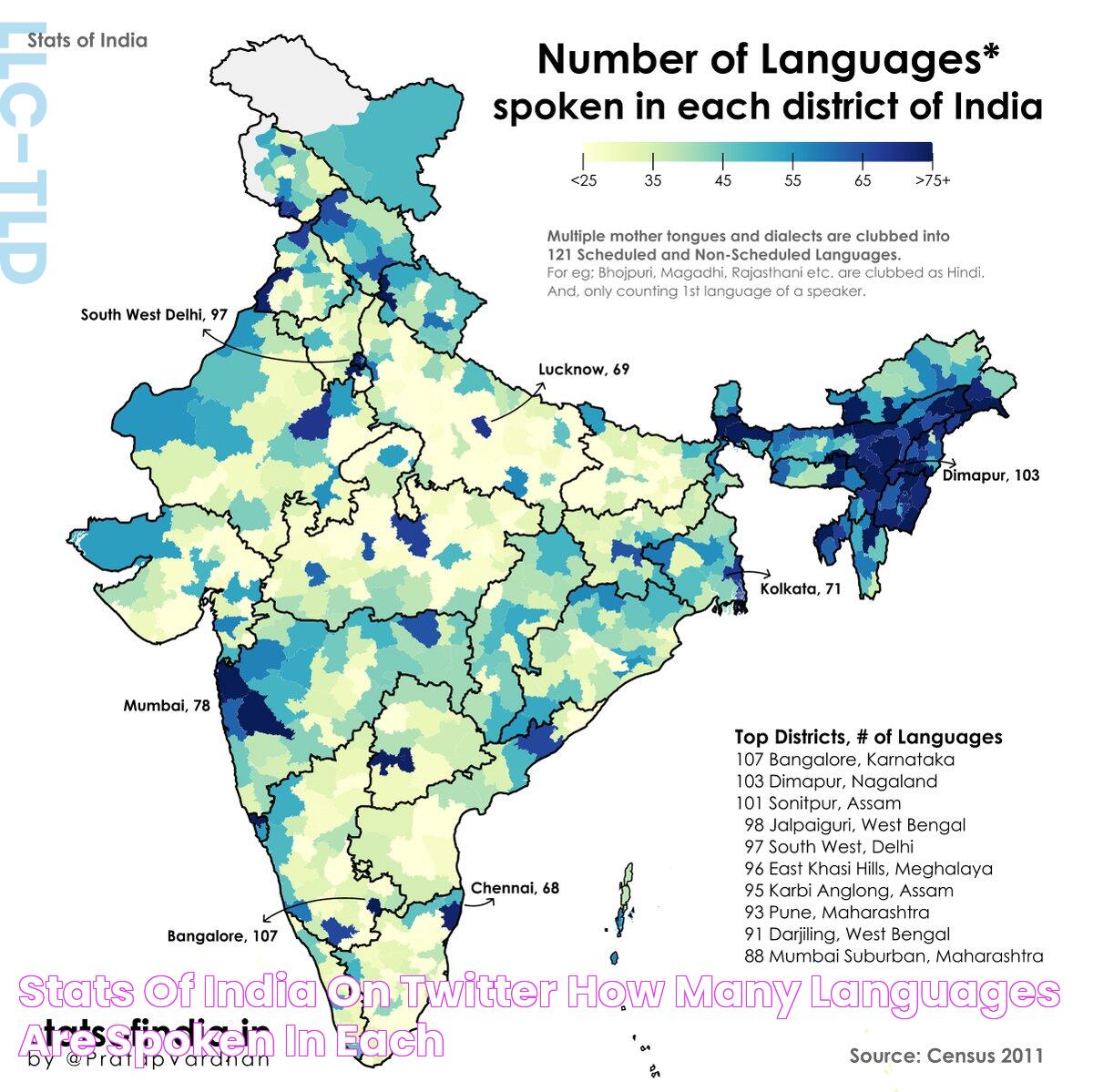
Estimates suggest that India is home to over 19,500 languages and dialects, though many are spoken by small communities. The People’s Linguistic Survey of India and Census data provide valuable insights into this linguistic diversity. However, when it comes to active, spoken languages, the number reduces significantly due to language shifts and assimilation.
The 2011 Census of India lists 121 languages spoken by 10,000 or more people. This includes major languages like Hindi and Bengali and lesser-known ones like Bhili and Gondi. The diversity is staggering, and each language adds to the richness of India’s cultural fabric.
Regional Languages and Their Cultural Significance
Regional languages in India are deeply intertwined with local traditions, music, literature, and art. For instance:
- Tamil: Known for its classical literature and Carnatic music.
- Bengali: Renowned for its poetry and films.
- Punjabi: Celebrated for its folk songs and dances like Bhangra.
Each region takes immense pride in its linguistic heritage, often seeing it as a cornerstone of cultural identity.
Role of Hindi and English in India
Hindi, spoken by over 40% of the population, serves as a national language for communication. English, on the other hand, acts as a link language, especially in business, education, and technology. Both languages play crucial roles in bridging linguistic divides in this diverse country.
What Are Scheduled Languages in India?
Scheduled Languages are those recognized by the Constitution of India. These languages receive support for development, promotion, and preservation. They also play a significant role in governance, education, and cultural preservation.
Endangered and Lost Languages
India is witnessing a decline in linguistic diversity, with many languages becoming endangered. UNESCO has listed several Indian languages as critically endangered, including Sema, Aka, and Tai Khamti. Efforts are underway to document and revive these languages.
How Do Languages Impact Education in India?
India’s education system accommodates linguistic diversity through its three-language formula, where students learn their regional language, Hindi, and English. This approach fosters inclusivity and broadens intellectual horizons.
Role of Linguistic Diversity in Governance
Linguistic diversity poses challenges in governance but also enriches democratic processes. India’s federal structure allows states to adopt their official languages, ensuring representation and cultural preservation.
How Do Languages Impact Indian Culture?
Languages are integral to Indian culture, influencing literature, cinema, cuisine, and festivals. They serve as a medium to pass down traditions, stories, and values from one generation to the next.
Languages and Technology in India
Technology is bridging linguistic gaps in India. From translation apps to regional content on social media, digital platforms are enabling more Indians to engage with their native languages.
Why Are Some Indian Dialects Misunderstood as Languages?
Dialects often evolve into distinct languages over time, but the distinction isn’t always clear. Sociopolitical factors, script development, and cultural identity often determine whether a dialect is considered a language.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How many languages are spoken in India? Over 19,500 languages and dialects, with 121 languages spoken by 10,000 or more people.
- What is the national language of India? India does not have a national language, but Hindi and English are used for official purposes.
- What are Scheduled Languages? These are 22 languages recognized by the Constitution of India.
- Are regional languages declining in India? Some are, but efforts are being made to preserve and promote them.
- What is India’s three-language formula? A policy encouraging the learning of a regional language, Hindi, and English in schools.
- How is technology impacting Indian languages? Technology is fostering inclusivity by providing regional content and translation tools.
Conclusion
India’s linguistic diversity is a testament to its rich cultural heritage and history. While challenges remain in preserving and promoting languages, the country’s efforts showcase its commitment to its linguistic roots. The question "how many languages are there in India?" doesn’t have a straightforward answer, but it opens the door to understanding the profound complexity and beauty of India’s linguistic landscape. Each language, dialect, and script adds a unique thread to the vibrant tapestry that is India.