Pitting edema occurs when pressure is applied to a swollen area, typically on the skin, and an indentation or "pit" remains even after the pressure is released. This characteristic is an indicator of excess fluid trapped in the tissues. The pitting edema scale helps quantify the extent of this indentation, providing a standardized method for clinicians to communicate and document the severity of edema. Moreover, the pitting edema scale not only serves as a diagnostic tool but also plays a role in monitoring the progress of treatment in patients with cardiovascular, renal, or hepatic conditions. By assessing changes in the degree of pitting, healthcare providers can evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and make necessary adjustments to the patient's care plan. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the pitting edema scale, offering valuable insights for both medical professionals and patients alike.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| 1. What is Pitting Edema? |
| 2. How is Pitting Edema Diagnosed? |
| 3. The Importance of the Pitting Edema Scale |
| 4. How to Use the Pitting Edema Scale? |
| 5. Different Grades in the Pitting Edema Scale |
| 5.1 What is Grade 1 Pitting Edema? |
| 5.2 What is Grade 2 Pitting Edema? |
| 5.3 What is Grade 3 Pitting Edema? |
| 5.4 What is Grade 4 Pitting Edema? |
| 6. Factors Contributing to Pitting Edema |
| 7. How is Pitting Edema Treated? |
| 8. Monitoring Pitting Edema in Patients |
| 9. Pitting Edema Scale in Clinical Practice |
| 10. Challenges in Using the Pitting Edema Scale |
| 11. FAQs |
| 12. Conclusion |
What is Pitting Edema?
Pitting edema is a type of swelling characterized by fluid accumulation in the body's tissues, most commonly observed in the legs, ankles, and feet. This condition occurs when there is an imbalance in the body's fluid retention mechanisms, often linked to various medical conditions. When pressure is applied to the affected area, such as pressing a finger on the skin, an indentation or "pit" forms and remains temporarily, hence the term "pitting" edema.
This condition is primarily a symptom rather than a disease in itself, indicating underlying health issues such as heart failure, kidney problems, or liver disorders. The severity and duration of pitting edema can vary, and understanding its causes is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Read also:Rutherford Electric Your Guide To Powering The Future
Recognizing pitting edema is essential for healthcare providers as it helps in diagnosing the root cause of the swelling and developing an appropriate treatment plan. Patients may also notice pitting edema as a symptom of prolonged sitting or standing, particularly in hot weather, which can exacerbate fluid retention in the lower extremities.
How is Pitting Edema Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pitting edema involves a combination of physical examination and, in some cases, additional diagnostic tests. During a physical examination, healthcare providers assess the affected area by applying pressure with a finger to determine the presence and severity of pitting.
In addition to the physical examination, medical history and symptoms reported by the patient play a crucial role in diagnosing pitting edema. Patients might be asked about recent weight gain, changes in diet, exercise habits, and any other symptoms like shortness of breath or fatigue.
Further diagnostic tests may be conducted to identify the underlying cause of pitting edema. These tests can include blood tests to assess kidney and liver function, imaging studies such as ultrasounds or X-rays to check for fluid accumulation, and electrocardiograms (ECG) to evaluate heart function.
The Importance of the Pitting Edema Scale
The pitting edema scale is an essential tool for healthcare professionals, providing a standardized method to assess and communicate the severity of edema. By quantifying the extent of pitting, the scale aids in determining the possible causes and the appropriate course of action for treatment.
This scale also plays a crucial role in monitoring the progress of treatment in patients with conditions that cause edema. By regularly assessing changes in the degree of pitting, healthcare providers can evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and make necessary adjustments to the patient's care plan.
Read also:Inter Miami Jersey A Symbol Of Passion And Style
Moreover, the pitting edema scale facilitates better communication among healthcare teams, ensuring that all members are on the same page regarding the patient's condition and treatment progress. This standardized approach helps in providing consistent and effective care for patients with edema.
How to Use the Pitting Edema Scale?
Using the pitting edema scale involves a simple yet effective method of assessing the severity of edema through physical examination. The scale is based on the depth of the indentation and the time it takes for the skin to return to its normal state after pressure is applied.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use the pitting edema scale:
- Ask the patient to sit or lie down comfortably, exposing the area with swelling.
- Apply gentle pressure to the swollen area, typically with the thumb, for about 5 seconds.
- Observe the indentation formed and note the depth and duration of the pit.
- Use the pitting edema scale to classify the severity based on your observations.
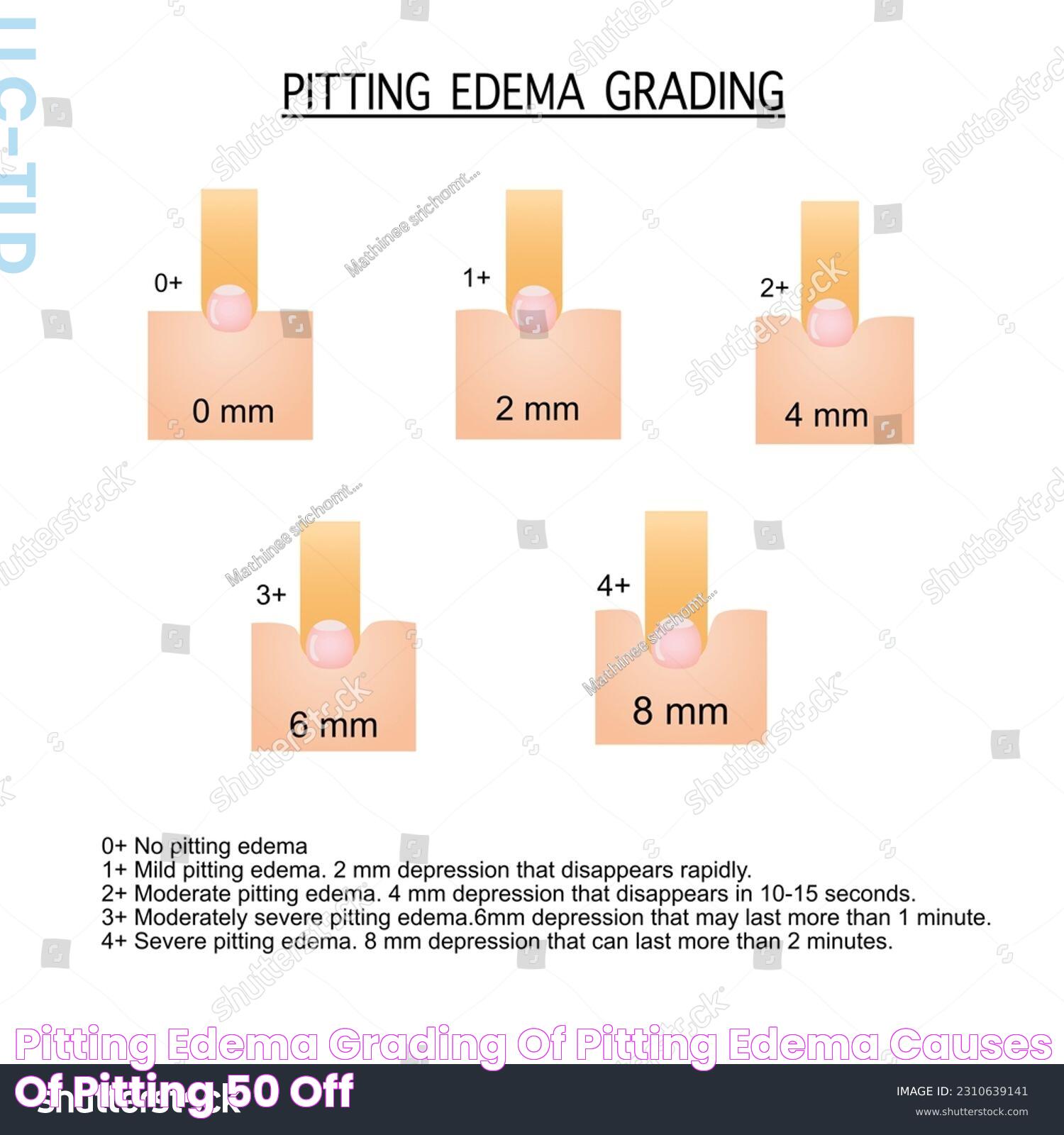
The pitting edema scale is divided into four grades, with Grade 1 indicating mild edema and Grade 4 indicating severe edema. Healthcare providers use this grading system to assess and document the patient's condition accurately.
Different Grades in the Pitting Edema Scale
The pitting edema scale is divided into four grades, each representing the severity of the condition based on the depth of the indentation and the time it takes to resolve. Understanding these grades helps in assessing the severity of edema and determining the appropriate course of treatment.
What is Grade 1 Pitting Edema?
Grade 1 pitting edema is the mildest form of pitting edema, characterized by a slight indentation that disappears quickly after pressure is released. In this stage, the pit depth is usually around 2mm or less, and the skin returns to its normal state almost immediately.
This grade of pitting edema is often temporary and may result from prolonged sitting or standing, especially in hot weather. It is usually not a cause for concern unless it persists or is accompanied by other symptoms.
What is Grade 2 Pitting Edema?
Grade 2 pitting edema involves a moderate level of swelling, with an indentation depth of approximately 4mm. The pit takes longer to resolve, typically lasting for about 10 to 15 seconds after the release of pressure.
This grade may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires attention, such as heart or kidney issues. It is essential for healthcare providers to evaluate the patient's overall health and consider additional tests to diagnose the cause of the edema.
What is Grade 3 Pitting Edema?
Grade 3 pitting edema is more severe, with an indentation depth of about 6mm. The pit remains for 30 seconds or more after the pressure is removed, indicating significant fluid retention in the tissues.
This grade often signals more serious health concerns, such as congestive heart failure or advanced kidney disease. Prompt medical evaluation and intervention are crucial to address the underlying condition and prevent complications.
What is Grade 4 Pitting Edema?
Grade 4 pitting edema is the most severe form, characterized by deep indentations of 8mm or more. The pits can last for over 30 seconds, indicating extensive fluid accumulation in the tissues.
This grade of edema is usually associated with critical medical conditions that require immediate attention and treatment. Patients with Grade 4 pitting edema often experience significant discomfort and may have additional symptoms such as difficulty breathing or extreme fatigue.
Factors Contributing to Pitting Edema
Several factors can contribute to the development of pitting edema, ranging from lifestyle choices to underlying medical conditions. Understanding these factors is essential for effective management and prevention of edema.
Common factors contributing to pitting edema include:
- Prolonged sitting or standing, leading to fluid accumulation in the legs.
- High sodium intake, causing the body to retain excess fluid.
- Poor circulation, often seen in individuals with cardiovascular issues.
- Kidney dysfunction, affecting the body's fluid balance.
- Liver disease, leading to fluid retention and swelling.
- Pregnancy, as hormonal changes and increased pressure on the veins can cause edema.
Identifying the contributing factors is crucial for healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan and address the root cause of the edema.
How is Pitting Edema Treated?
Treating pitting edema involves addressing the underlying cause and implementing measures to reduce fluid retention in the body. The treatment plan may vary depending on the severity of the edema and the patient's overall health condition.
Common treatment options for pitting edema include:
- Lifestyle modifications, such as reducing sodium intake and engaging in regular physical activity to improve circulation.
- Compression therapy, using compression stockings or bandages to help reduce swelling.
- Medications, such as diuretics, to help the body eliminate excess fluid.
- Elevating the affected limbs to reduce fluid accumulation.
- Treating the underlying medical condition, such as heart or kidney disease, to prevent recurrence of edema.
Close monitoring and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make necessary adjustments as needed.
Monitoring Pitting Edema in Patients
Monitoring pitting edema in patients involves regular assessments to evaluate the severity of the condition and the progress of treatment. This process is crucial for ensuring that the treatment plan is effective and for making necessary adjustments to improve patient outcomes.
Healthcare providers use the pitting edema scale to monitor changes in the degree of pitting and document these findings in the patient's medical records. Regular monitoring helps in identifying any worsening of the condition and enables timely intervention to prevent complications.
In addition to using the pitting edema scale, healthcare providers may also track other symptoms and conduct additional tests to evaluate the patient's overall health and the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
Pitting Edema Scale in Clinical Practice
The pitting edema scale is widely used in clinical practice as a reliable tool for assessing and documenting the severity of edema in patients. Its standardized approach allows healthcare providers to communicate effectively and ensure consistent care for patients with edema.
In clinical settings, the pitting edema scale is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools to evaluate the patient's condition comprehensively. This approach helps in identifying the underlying cause of the edema and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
The pitting edema scale is also valuable in research settings, where it is used to study the prevalence and impact of edema in various patient populations. This information can inform clinical guidelines and improve patient care outcomes.
Challenges in Using the Pitting Edema Scale
While the pitting edema scale is a valuable tool, there are challenges associated with its use in clinical practice. One of the main challenges is the subjective nature of the assessment, as the depth of the indentation and the time it takes to resolve can vary depending on the examiner's technique and judgment.
Additionally, the pitting edema scale may not accurately reflect the severity of edema in patients with chronic conditions or those with non-pitting edema, where the skin does not retain an indentation after pressure is applied.
To overcome these challenges, healthcare providers should receive proper training in using the pitting edema scale and consider other diagnostic tools and tests to assess the patient's condition accurately.
FAQs
What causes pitting edema?
Pitting edema is caused by fluid retention in the body's tissues, often due to underlying medical conditions such as heart failure, kidney disease, or liver disorders. It can also result from prolonged sitting or standing, high sodium intake, or poor circulation.
How is pitting edema different from non-pitting edema?
Pitting edema is characterized by an indentation or "pit" that remains after pressure is applied to the swollen area. Non-pitting edema, on the other hand, does not retain an indentation and is often associated with conditions like lymphedema or hypothyroidism.
Can pitting edema be prevented?
While not all cases of pitting edema can be prevented, certain lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk. These include maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and managing underlying health conditions.
Is pitting edema a serious condition?
Pitting edema itself is not a disease but a symptom of an underlying condition. While mild cases may not be serious, persistent or severe pitting edema can indicate significant health issues that require medical attention and treatment.
How is the severity of pitting edema assessed?
The severity of pitting edema is assessed using the pitting edema scale, which measures the depth of the indentation and the time it takes to resolve after pressure is applied. The scale is divided into four grades, with Grade 1 indicating mild edema and Grade 4 indicating severe edema.
What is the role of the pitting edema scale in treatment?
The pitting edema scale plays a crucial role in treatment by providing a standardized method for assessing the severity of edema. This information helps healthcare providers determine the appropriate course of treatment and monitor the progress of interventions over time.
Conclusion
The pitting edema scale is an invaluable tool in the medical field, offering a standardized approach to assessing and documenting the severity of edema. By understanding the different grades of this scale, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose and treat the underlying causes of pitting edema, ensuring improved patient outcomes.
From assessing mild cases of edema resulting from lifestyle factors to identifying severe cases indicative of critical health conditions, the pitting edema scale serves as a crucial component of patient care. Its role in monitoring treatment progress further emphasizes its importance in clinical practice.
Ultimately, the pitting edema scale not only aids healthcare providers in delivering consistent and effective care but also empowers patients with a better understanding of their condition and the necessary steps to manage it. As we continue to advance in medical research and practice, the pitting edema scale remains a cornerstone in the assessment and treatment of fluid retention conditions.